

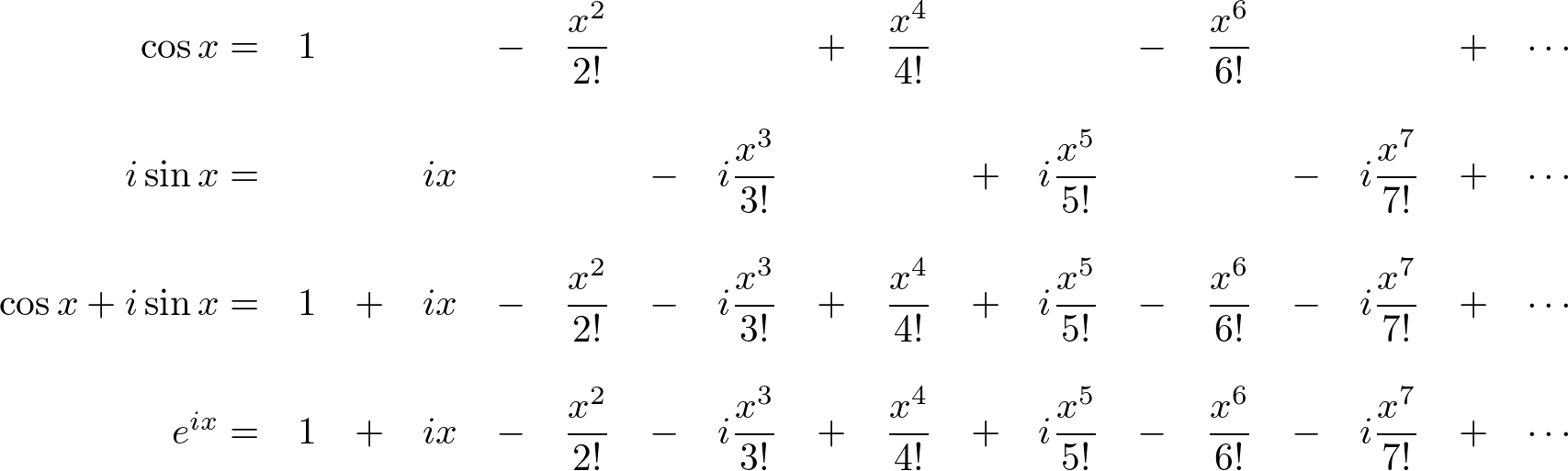
Students will need to expand the Taylor series formula when approximating a function. The first is simply the expanded version of the other. If a = 0, the Taylor series becomes the McLaurin Series, another special power seriesīoth formulas are the same and are sufficient when using the series to determine power function behavior. The Taylor Series of Function f(x), which is infinitely differentiable at a centered real or complex number denoted by a is the power series The Taylor series becomes the Mclaurin series when a = 0. The Taylor series is an approximation of a function whose accuracy gets better as n increases at a constant point of a. In this piece, students will learn the Taylor Series formula and how to apply it when calculating the approximations of power functions. For example, students who want to want to determine the derivative of a function polynomial degree of 6, will only need to compute the 6th sum of terms (n + 1) using the Taylor series. Using the Taylor series, students will only need to determine the n + 1 terms of the nth polynomial in the power function. For the Taylor series to work, the functions will need to be expressed as derivatives at a sine point. The Taylor series makes it easy for students to determine the behaviour of the power functions as it represents their infinite sum of terms. The Taylor series actually help students know how the different functions mentioned above behave. The sin function, cosine function and Hyperbolic functions are different power series. The exponential function is a popular power function, but that is not all there is to it. Now, power functions are special functions with a power greater than 1 and moving towards infinity. The Taylor series is a special Power series designed to show mathematicians how power series behave.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
